Magnetic domain and Magnetic Induction
Magnetic Domain
A magnet is made up of many magnetic domains.
Magnetic domain is a group of atomic magnets pointing in
the same direction.Atomic magnet is represented by an arrow with arrowhead as a
North pole and tail as a South Pole.
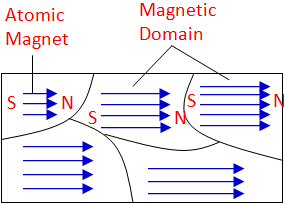
In a magnetized bar, the magnetic domains are all pointed in the same
direction as shown above. The North and South poles of adjacent domains
cancel each other out except the poles at the both ends, and hence producing
North and South poles at the ends.
Note that every magnet has a maximum strength. We say it is magnetically
saturated and cannot be any stronger. This occurs when all the
magnetic domains pointed in one direction.
Magnetic Induction
Magnetic induction is a process where a magnetic material becomes
an induced magnet when it is brought near to or in contact
with a magnet.
Process
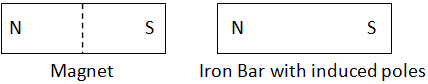
The magnetic material (i.e iron bar) becomes an induced magnet with
the end nearer the magnet having opposite pole to that of the
magnet. Thus, it is attracted to the magnet as unlike poles attract.
Note
- Magnetic induction has to occur before the attraction of magnetic material by a magnet.
Types of Magnetic Material
|
Soft Magnetic Material |
Hard Magnetic Material |
|
Easy to be magnetized and demagnetized |
Hard to be magnetized and demagnetized |
|
Do not retain its magnetism |
Retain its magnetism |
|
To make temporary magnets like electromagnets used in a scrapyard. |
To make permanent magnets like magnetic door catch. |
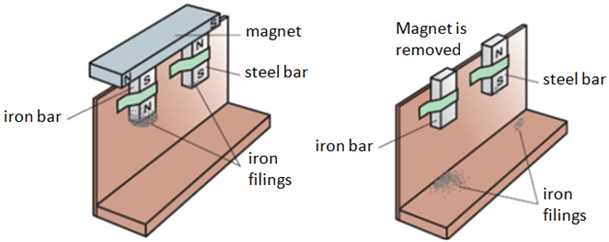
The following diagram shows the difference in the magnetic properties of Soft Magnetic Material (Iron) and Hard Magnetic Material (Steel).
Example
The diagram shows an aquarium magnetic cleaner which would clean both sides of
the fish tank at the same time. When the magnet A is moved over the
outside surface, magnet B would follow it by moving over the inside
surface.
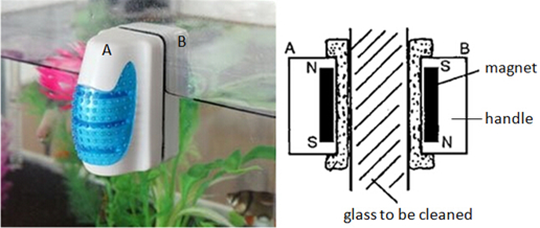
(a) Explain why B follows the movement of A.
(b) Explain why there is a practical limit to the thickness of the fish
tank glass for the device to work.
(c) When A and B are placed on opposite sides of a vertical sheet of iron, B
remains where it is even when A is removed. Suggest a reason for this.
Answer:
(a) Magnet A and B have opposite poles facing each other. Thus, B follows the
movement of A as unlike poles attract each other.
(b) Magnetic field strength becomes weaker when the window is too thick, hence
the magnets may no longer attract each other strongly and be held in place.
(c) The iron sheet is induced with poles opposite to that of the magnetic pole
next to it. Hence attraction still occurs.